What is Actinium-PSMA?
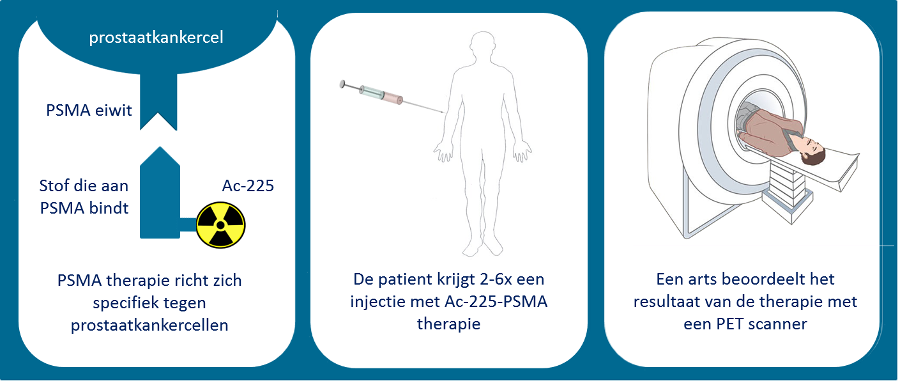
The therapy
A commonly used alpha emitter is Actinium-225 (Ac-225). When this Ac-225 is linked to a substance that specifically binds to PSMA on the tumor cells, the Ac-225 can destroy the cancer cells to which it is bound. Alpha emitters cause double-stranded DNA damage, unlike the single-stranded DNA damage of beta emitters. Due to this, alpha emitters are more powerful when irradiation tumor cells, yet will also have increased side effects As a result, Ac-225-PSMA appears to have a stronger antitumor effect than Lu-177-PSMA. Thus, it is hypothesized that patients who no longer respond to Lu-177-PSMA may still respond to Ac-225-PSMA. However, treatment with Ac-225-PSMA is still experimental. Globally, there is a lot of scientifc interest in Ac-225-PSMA, such as at the Erasmus MC.
Side Effects
Most published studies discussing Ac-225-PSMA therapy have been conducted on patients who have already received many treatments and are approaching the end of their lives. The data involving Ac-225-PSMA in earlier disease stages is very limited. Studies have shown that a dose of 100 KBq Ac-225-PSMA per kg body weight is currently best with a maximum effect and tolerable side effects. The largest study with 40 participants does show that many patients had such side effects to the salivary glands (permanent/ severe dry mouth) that therapy had to be discontinued. However, side effects reports vary widely between different publications. For example, a study from South Africa reported no serious (grade 3/4) side effects to the salivary glands.
The kidneys and bone marrow are also at risk with Ac-225-PSMA therapy. However, no study has reported grade 3/4 toxicity to these organs. Long-term side effects of Ac-225-PSMA therapy are not yet known.
Because of worldwide scarcity of Ac-225 and the severe dry mouth that can occur after Ac-225-PSMA, combination treatment of Lu-177-PSMA with a low dose of Ac-225-PSMA (so-called tandem therapy) is now also being studied. Because of worldwide scarcity of Ac-225 and the severe dry mouth that can occur after Ac-225-PSMA, combination treatment of Lu-177-PSMA with a low dose of Ac-225-PSMA (so-called tandem therapy) is now also being studied.
Rules of Life
The rules for Ac-225-PSMA therapy differ per country. When looking only at the radiation a patient emits after the therapy, there is no need to stay in the hospital: alpha emitter radiation has a range of only a few micrometers and will therefore not pass outside the patient’s body. This means that there is no danger to loved ones. However, most of the Ac-225-PSMA leaves the body through the urine. When the patient is at home, the radioactive radiation will end up in the sewer via the toilet. The disadvantage of the short range of alpha emitters is that they are very difficult to measure and therefore difficult to detect. In the Netherlands, patients will therefore stay in the hospital for 24 hours after the injection of the therapy. The radioactive urine is collected and stored in special tanks until the radioactivity has expired. That way it doesn’t end up in the environment. After 24 hours, more than 90% of the radioactive substance has left the body. The patient can then go home.